diff --git a/plugin-tutorial/examples/python-rag_memo-stdio.md b/plugin-tutorial/examples/python-rag_memo-stdio.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..a9f96ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/plugin-tutorial/examples/python-rag_memo-stdio.md
@@ -0,0 +1,392 @@
+# Building a RAG-Based Memory Storage MCP Server in Python
+
+[Tutorial Code Repository](https://github.com/Dormiveglia-elf/rag_memo_mcp)
+
+## Introduction
+
+In this tutorial, we'll demonstrate how to build a simple RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) based long-term memory storage MCP server using Python, and debug it using the [openmcp](https://github.com/LSTM-Kirigaya/openmcp-client) plugin. Once implemented, we'll be able to store, retrieve, and manage our memories through natural language interactions with large language models, without needing to write any specific query code.
+
+## 1. Setup
+
+The project structure is as follows:
+
+```bash
+📦rag_memo_mcp
+ ┣ 📂memory_db/ # LanceDB database files, created during initialization
+ ┣ 📜server.py # MCP server implementation
+ ┣ 📜pyproject.toml # Project configuration file
+ ┣ 📜uv.lock # uv lockfile
+ ┗ ...
+```
+
+First, let's prepare the runtime environment. This project recommends using [uv](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv). (`uv` is a blazingly fast Python package manager that's beloved by those who use it. Of course, if you're a loyal fan of `pip` or other package managers, that works perfectly fine too.)
+
+```bash
+# First download uv (Windows)
+powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
+# Or (macOS/Linux)
+# curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
+```
+
+```bash
+# Project initialization
+uv init rag_memo_mcp
+cd rag_memo_mcp
+# We recommend creating a virtual environment
+uv venv
+# Activate virtual environment (Windows)
+.venv\Scripts\activate
+# Or (macOS/Linux)
+# source .venv/bin/activate
+
+# Install dependencies
+uv add "mcp[cli]" lancedb pandas sentence-transformers
+```
+
+## 2. Understanding the Service Implementation
+
+Unlike traditional databases that require pre-installation and configuration, this project's core `MemoryStore` uses [LanceDB](https://lancedb.github.io/), a vector database that automatically creates and initializes itself in the `memory_db` directory when the server first starts, requiring no additional configuration.
+
+Let's dive into `server.py` to understand its implementation details.
+
+### 2.1 MemoryStore Core Class
+
+The `MemoryStore` class is the heart of memory storage and retrieval functionality.
+
+```python
+class MemoryStore:
+```
+
+- **`initialize()`**: This method handles initialization. It connects to the LanceDB database (creating it if it doesn't exist), defines the memory table schema, and by default loads the `all-MiniLM-L6-v2` model for generating vector embeddings from text content.
+
+```python
+def __init__(self, db_path: str = "./memory_db"):
+ self.db_path = db_path
+ self.db = None
+ self.table = None
+ self.encoder = None
+ self._initialized = False
+
+async def initialize(self):
+ if self._initialized:
+ return
+
+ self.encoder = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
+
+ self.db = lancedb.connect(self.db_path)
+
+ schema = pa.schema(
+ [
+ pa.field("id", pa.string()),
+ pa.field("content", pa.string()),
+ pa.field("summary", pa.string()),
+ pa.field("tags", pa.list_(pa.string())),
+ pa.field("timestamp", pa.timestamp("us")),
+ pa.field("category", pa.string()),
+ pa.field("importance", pa.int32()),
+ pa.field(
+ "vector", pa.list_(pa.float32(), 384)
+ ),
+ ]
+ )
+
+ try:
+ self.table = self.db.open_table("memories")
+ except Exception:
+ self.table = self.db.create_table("memories", schema=schema)
+
+ self._initialized = True
+```
+
+- **`store_memory()`**: When storing a new memory, this method generates a unique ID and timestamp for the memory content. If no summary is provided, it automatically generates a simple summary, then uses the pre-loaded model to convert the content into a vector, and finally stores all information (ID, content, summary, tags, timestamp, category, importance, vector) in the LanceDB table.
+
+```python
+async def store_memory(
+ self,
+ content: str,
+ summary: Optional[str] = None,
+ tags: Optional[List[str]] = None,
+ category: str = "general",
+ importance: int = 5,
+) -> str:
+ await self.initialize()
+
+ memory_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
+ timestamp = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
+
+ if not summary:
+ summary = content[:100] + "..." if len(content) > 100 else content
+
+ embedding = self._generate_embedding(content)
+
+ data = [
+ {
+ "id": memory_id,
+ "content": content,
+ "summary": summary,
+ "tags": tags or [],
+ "timestamp": timestamp,
+ "category": category,
+ "importance": importance,
+ "vector": embedding,
+ }
+ ]
+
+ self.table.add(data)
+
+ return memory_id
+```
+
+- **`search_memories()`**: This is the key to implementing RAG. When a query is made, this method converts the query text into a vector as well, then performs vector similarity search in LanceDB to find the most relevant memories. It also supports filtering by category and importance.
+
+```python
+async def search_memories(
+ self,
+ query: str,
+ limit: int = 10,
+ category: Optional[str] = None,
+ min_importance: Optional[int] = None,
+) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
+ await self.initialize()
+ query_embedding = self._generate_embedding(query)
+
+ search_query = self.table.search(query_embedding)
+
+ if limit:
+ search_query = search_query.limit(limit)
+
+ filters = []
+ if category:
+ filters.append(f"category = '{category}'")
+ if min_importance is not None:
+ filters.append(f"importance >= {min_importance}")
+
+ if filters:
+ filter_str = " AND ".join(filters)
+ search_query = search_query.where(filter_str)
+
+ results = search_query.to_pandas()
+
+ memories = []
+ for _, row in results.iterrows():
+ memory = {
+ "id": row["id"],
+ "content": row["content"],
+ "summary": row["summary"],
+ "tags": row["tags"].tolist(),
+ "timestamp": row["timestamp"],
+ "category": row["category"],
+ "importance": int(row["importance"]),
+ "similarity_score": row.get(
+ "_distance", 0.0
+ ),
+ }
+ memories.append(memory)
+
+ return memories
+```
+
+### 2.2 MCP Server and Tools
+
+We use `FastMCP` to quickly build an MCP server and expose `MemoryStore` functionality as tools that large language models can call through the `@mcp.tool()` decorator.
+
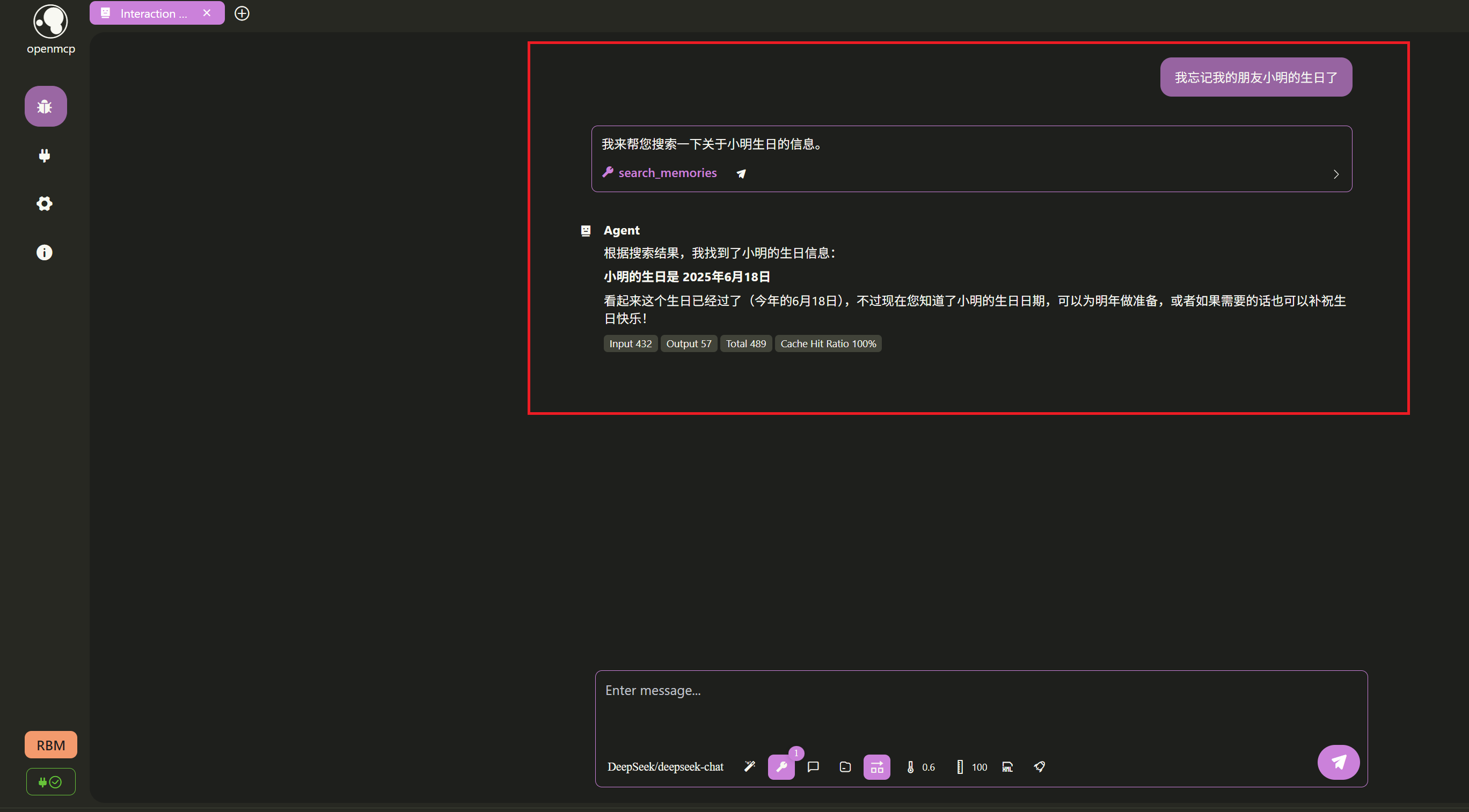
+- **`store_memory`**: **Take notes!** Store a memory.
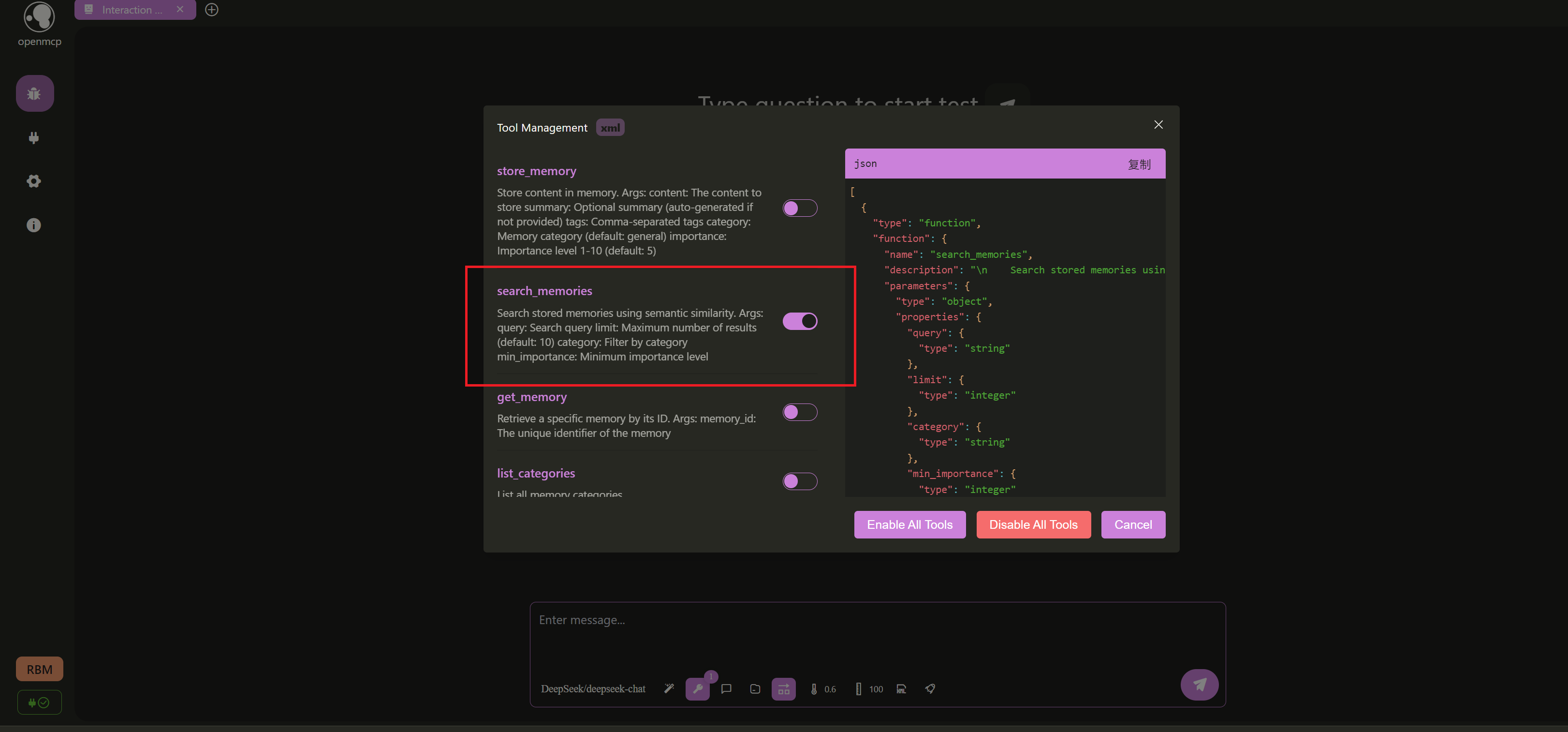
+- **`search_memories`**: **Let me think...** Search for relevant memories based on query content.
+- **`get_memory`**: **Find by reference!** Retrieve a specific memory by ID.
+- **`list_categories`**: **Organize by category!** List all memory categories.
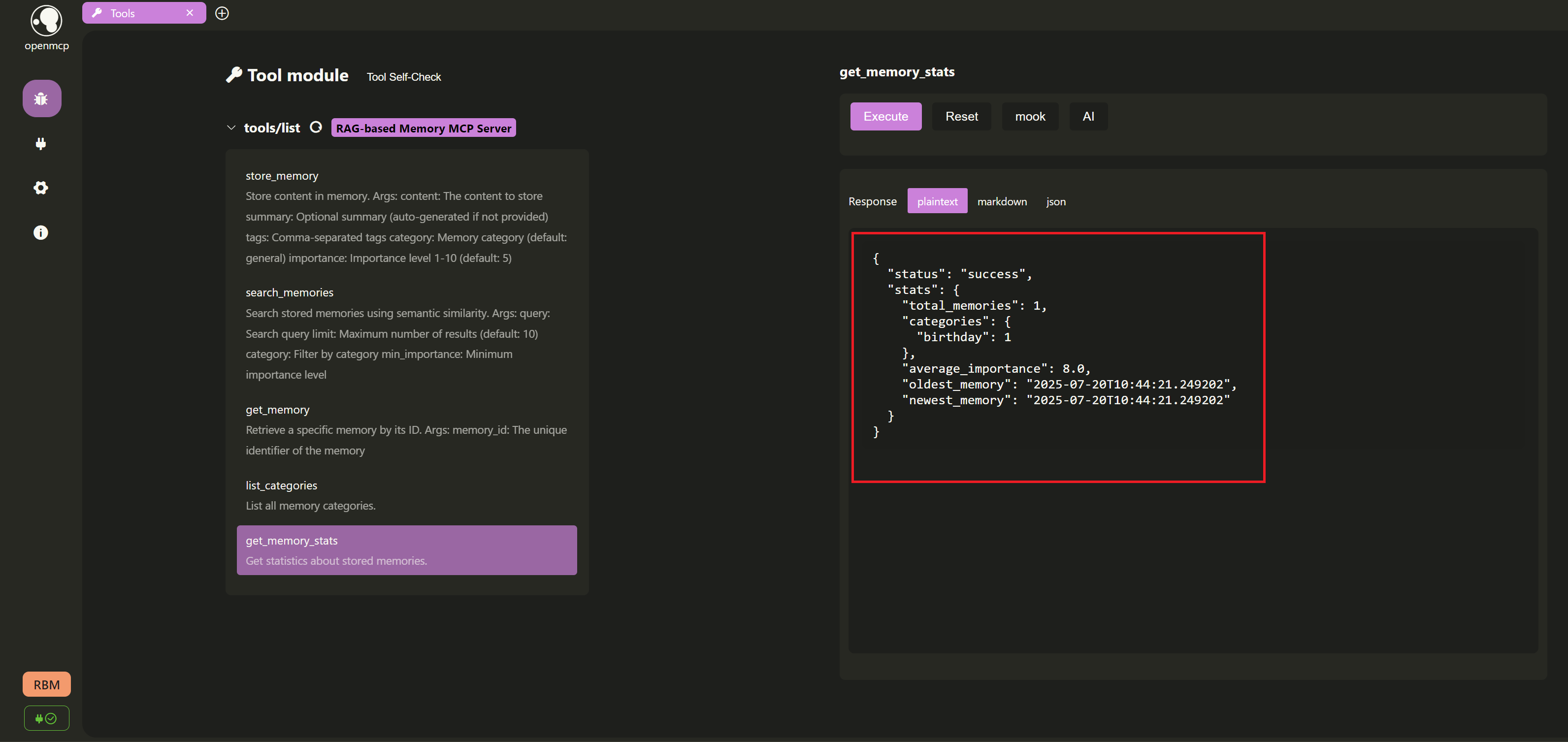
+- **`get_memory_stats`**: **Memory inventory!** Get statistics about the memory store, such as total count, counts by category, etc.
+
+```python
+# Initialize memory store
+memory_store = MemoryStore()
+
+# Create MCP server
+mcp = FastMCP("RAG-based Memory MCP Server")
+
+
+@mcp.tool()
+async def store_memory(
+ content: str,
+ summary: Optional[str] = None,
+ tags: Optional[str] = None,
+ category: str = "general",
+ importance: int = 5,
+) -> Dict[str, str]:
+ """
+ Store content in memory.
+
+ Args:
+ content: The content to store
+ summary: Optional summary (auto-generated if not provided)
+ tags: Comma-separated tags
+ category: Memory category (default: general)
+ importance: Importance level 1-10 (default: 5)
+ """
+ try:
+ # Parse tags if provided
+ tag_list = [tag.strip() for tag in tags.split(",")] if tags else []
+
+ memory_id = await memory_store.store_memory(
+ content=content,
+ summary=summary,
+ tags=tag_list,
+ category=category,
+ importance=importance,
+ )
+
+ return {
+ "status": "success",
+ "memory_id": memory_id,
+ "message": f"Memory stored successfully with ID: {memory_id}",
+ }
+ except Exception as e:
+ return {"status": "error", "message": f"Failed to store memory: {str(e)}"}
+
+
+@mcp.tool()
+async def search_memories(
+ query: str,
+ limit: int = 10,
+ category: Optional[str] = None,
+ min_importance: Optional[int] = None,
+) -> Dict[str, Any]:
+ """
+ Search stored memories using semantic similarity.
+
+ Args:
+ query: Search query
+ limit: Maximum number of results (default: 10)
+ category: Filter by category
+ min_importance: Minimum importance level
+ """
+ try:
+ memories = await memory_store.search_memories(
+ query=query, limit=limit, category=category, min_importance=min_importance
+ )
+
+ return {
+ "status": "success",
+ "query": query,
+ "total_results": len(memories),
+ "memories": memories,
+ }
+ except Exception as e:
+ return {"status": "error", "message": f"Search failed: {str(e)}"}
+
+
+@mcp.tool()
+async def get_memory(memory_id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
+ """
+ Retrieve a specific memory by its ID.
+
+ Args:
+ memory_id: The unique identifier of the memory
+ """
+ try:
+ memory = await memory_store.get_memory_by_id(memory_id)
+
+ if memory:
+ return {"status": "success", "memory": memory}
+ else:
+ return {
+ "status": "error",
+ "message": f"Memory with ID {memory_id} not found",
+ }
+ except Exception as e:
+ return {"status": "error", "message": f"Failed to retrieve memory: {str(e)}"}
+
+
+@mcp.tool()
+async def list_categories() -> Dict[str, Any]:
+ try:
+ categories = await memory_store.list_categories()
+ return {"status": "success", "categories": categories}
+ except Exception as e:
+ return {"status": "error", "message": f"Failed to list categories: {str(e)}"}
+
+
+@mcp.tool()
+async def get_memory_stats() -> Dict[str, Any]:
+ try:
+ stats = await memory_store.get_stats()
+ return {"status": "success", "stats": stats}
+ except Exception as e:
+ return {"status": "error", "message": f"Failed to get stats: {str(e)}"}
+```
+
+The server startup code is at the end of `server.py`, which first initializes the `MemoryStore`, then runs the MCP server.
+
+```python
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ # Initialize memory store on startup
+ async def init_memory():
+ await memory_store.initialize()
+
+ # Run initialization
+ asyncio.run(init_memory())
+
+ # Run MCP server
+ mcp.run()
+```
+
+## 3. Debugging with [openmcp](https://github.com/LSTM-Kirigaya/openmcp-client)
+
+### 3.1 Adding Workspace Connection
+
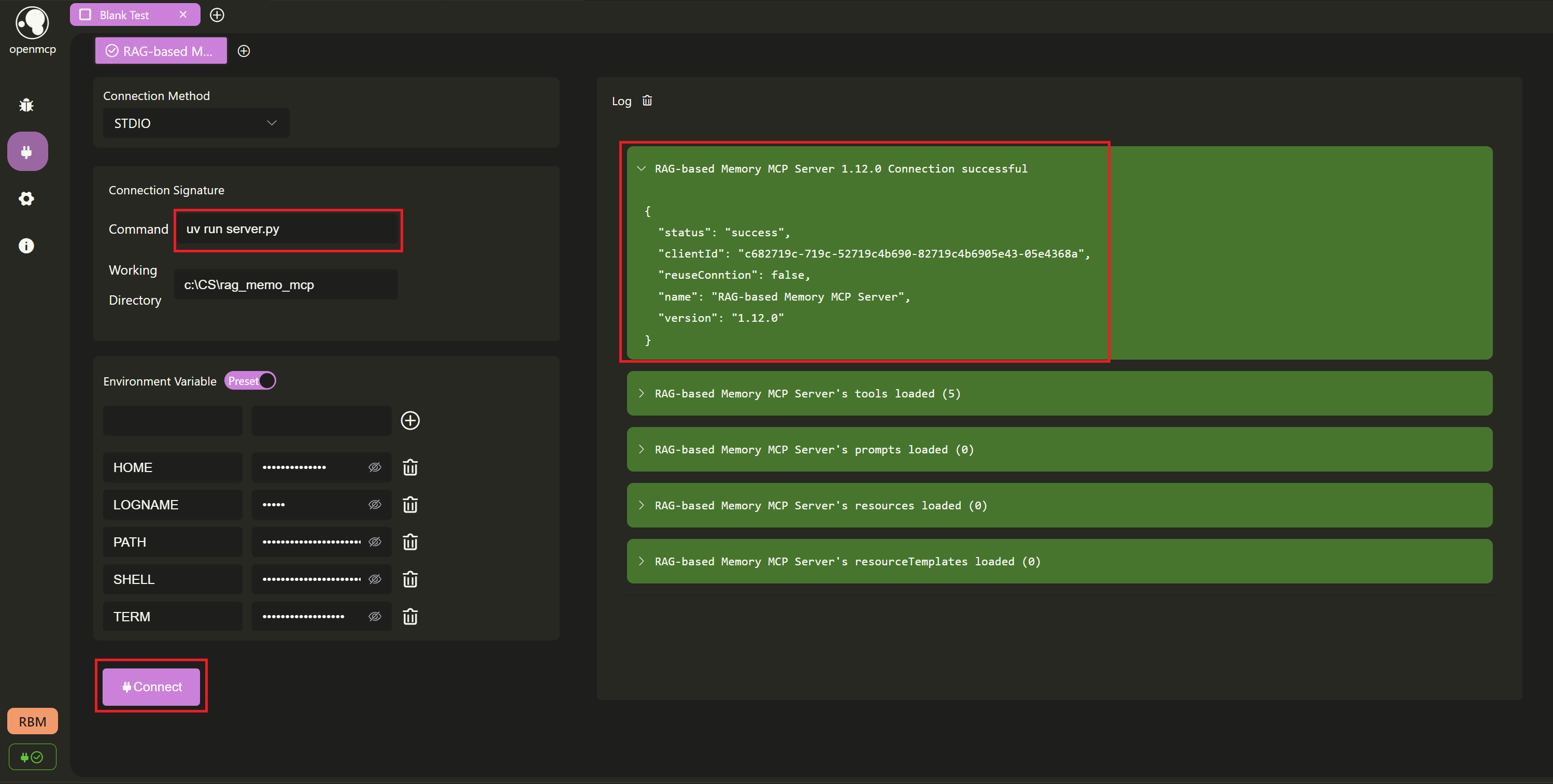
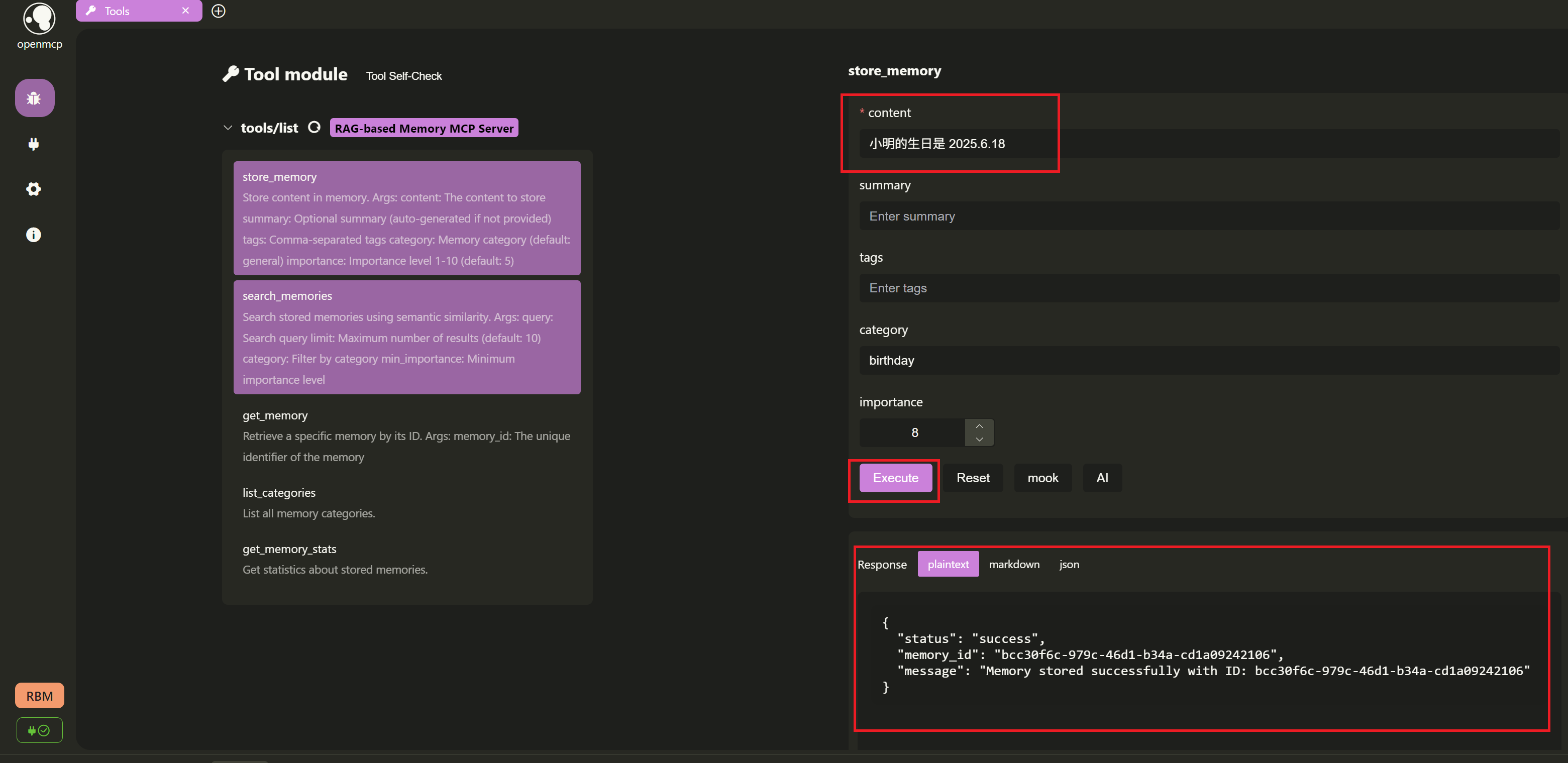
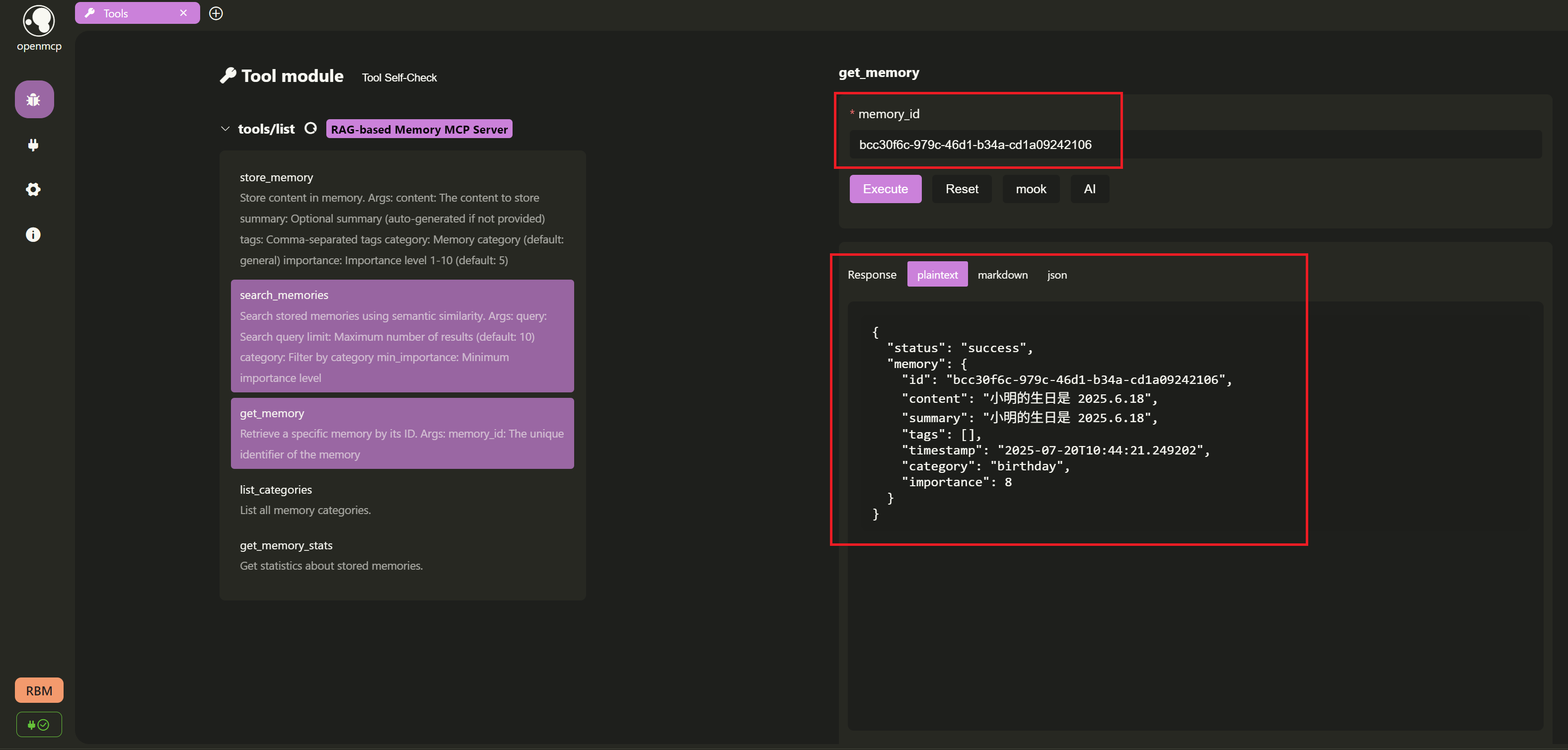
+Next, we'll debug using the [openmcp](https://github.com/LSTM-Kirigaya/openmcp-client) plugin. First, let's test if we can connect successfully. Here we choose `stdio`, set the working path to the project directory, then click `Connect`. In the log panel on the right, we can see that we've successfully connected.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+

+
+

+
 +
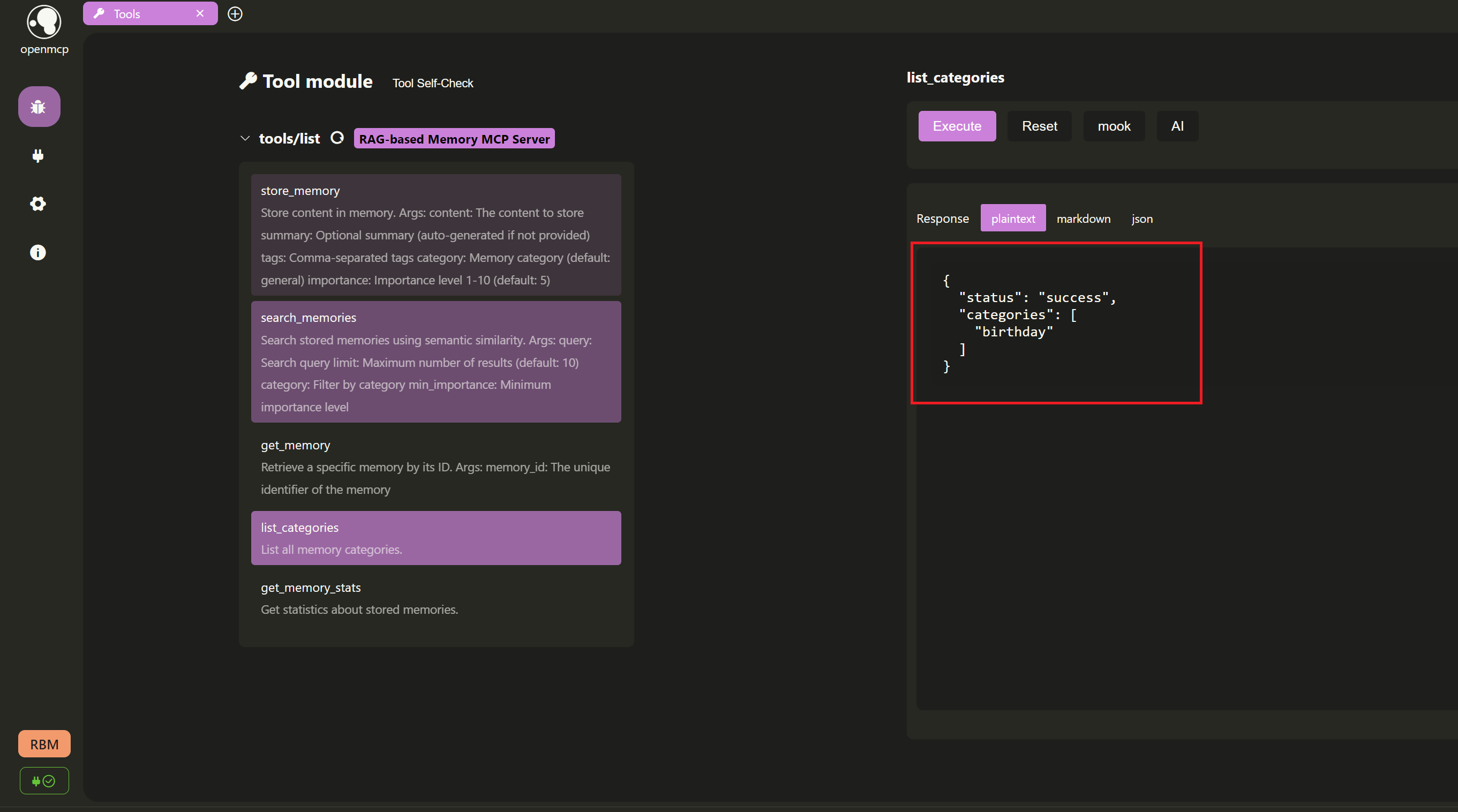
+3. **列出目前的记忆分类**:
+ 我们调用 `list_categories` 工具来查看当前所有记忆的分类。由于我们只添加了一个 `birthday` 分类的记忆,所以返回结果中应该只包含这个分类。
+
+
+
+3. **列出目前的记忆分类**:
+ 我们调用 `list_categories` 工具来查看当前所有记忆的分类。由于我们只添加了一个 `birthday` 分类的记忆,所以返回结果中应该只包含这个分类。
+
+
+

+
+

+
+

+
+

+
 +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+3. **列出目前的记忆分类**:
+ 我们调用 `list_categories` 工具来查看当前所有记忆的分类。由于我们只添加了一个 `birthday` 分类的记忆,所以返回结果中应该只包含这个分类。
+
+
+
+3. **列出目前的记忆分类**:
+ 我们调用 `list_categories` 工具来查看当前所有记忆的分类。由于我们只添加了一个 `birthday` 分类的记忆,所以返回结果中应该只包含这个分类。
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+