5.7 KiB
Implementing a Weather Information MCP Server in Python
The Problem Scenario
Before we begin, consider this common situation: I'm planning to attend the Arknights "Rusty Shadows" convention next Saturday in Hangzhou and want to check the weather forecast. When I ask an LLM about Saturday's weather, I get this response:
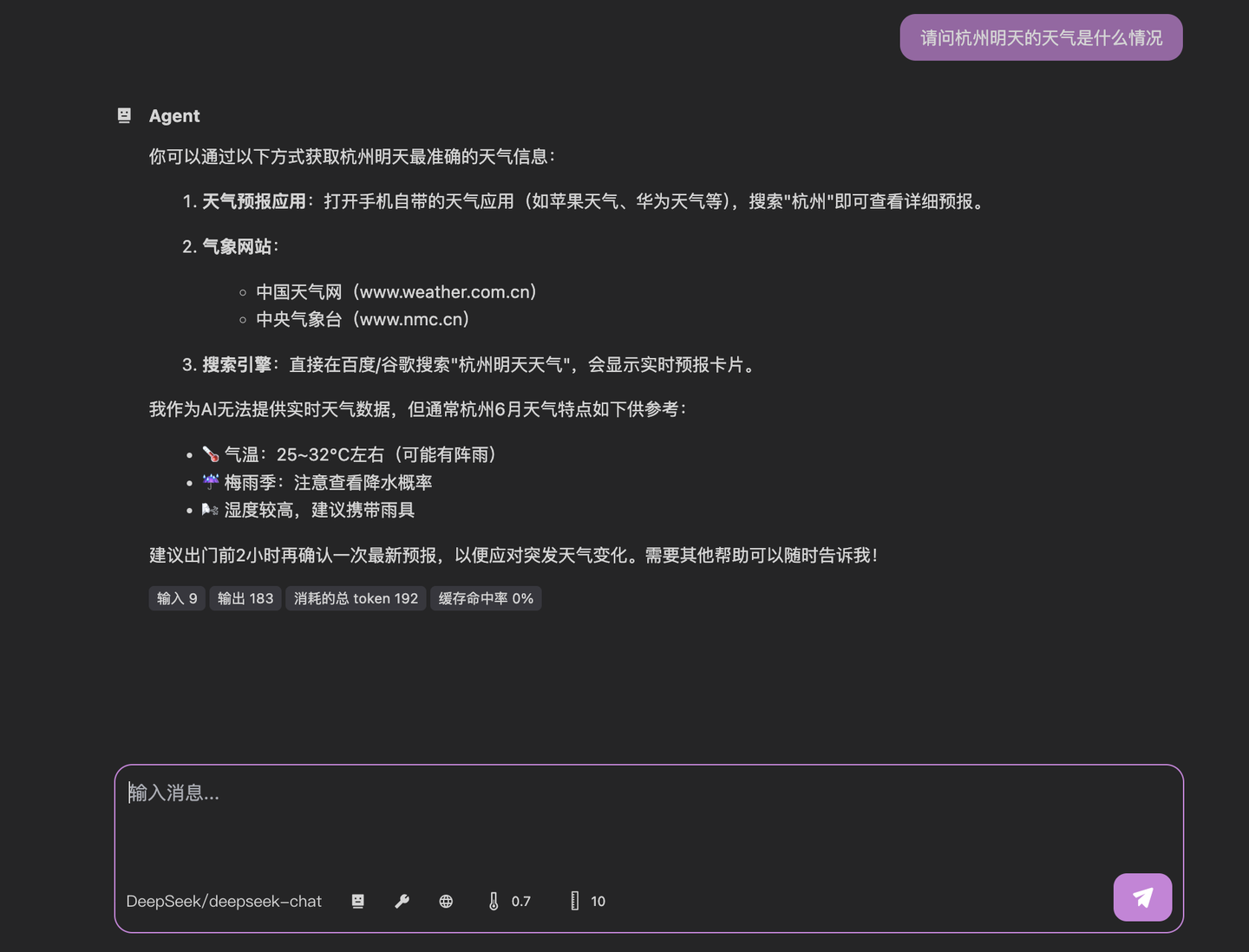
This "teach you to fish" approach isn't helpful for simple everyday queries. While there are many weather apps available, how can we integrate weather data directly into LLMs to get actionable answers?
Introduction
In our last tutorial, we covered MCP fundamentals. Now, we'll develop our first MCP server to bridge existing applications/services with LLMs.
For efficient development, we'll use OpenMCP - an integrated MCP testing tool I recently open-sourced:
OpenMCP Announcement
OpenMCP GitHub: https://github.com/LSTM-Kirigaya/openmcp-client
(Stars appreciated! :D)
Initial Setup
First, install the UV tool (a Conda alternative):
pip install uv
uv # Verify installation
Create a new project:
mkdir simple-mcp && cd simple-mcp
uv init
uv add mcp "mcp[cli]"
Install the OpenMCP plugin in VSCode:
Basic MCP Server
Create simple_mcp.py:
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP('Weather MCP Server', version="1.0.0")
@mcp.tool(
name='weather',
description='Get weather information for specified city'
)
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""Weather query protocol - returns formatted string"""
return f"Weather in {city}: Sunny, 25°C"
# Additional example tools/resources omitted for brevity
Test the server:
uv run mcp run simple_mcp.py
Connecting with OpenMCP
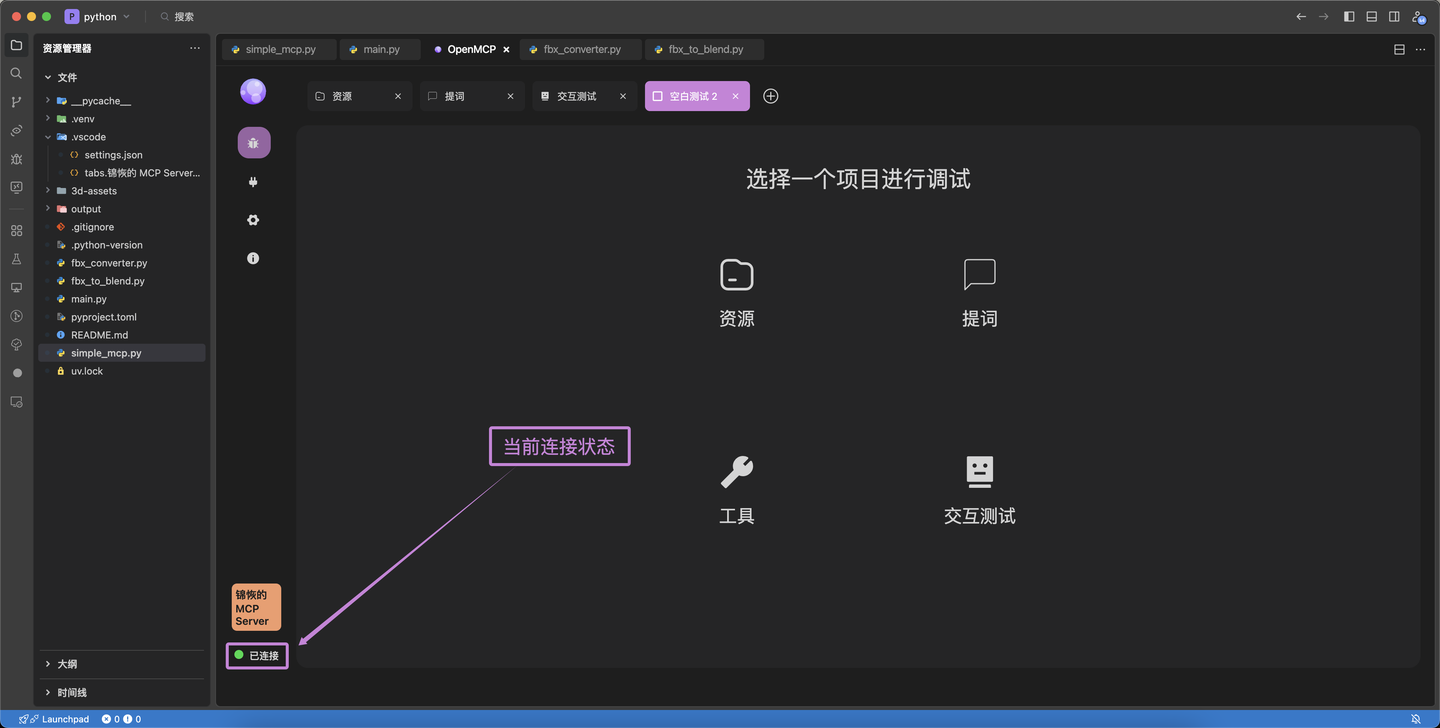
Click the purple OpenMCP icon in VSCode to launch the debugger. Verify connection status (green indicator):
Developing the Weather Function
Tool Debugging
Our initial weather tool just returns static data. Let's test it in OpenMCP:
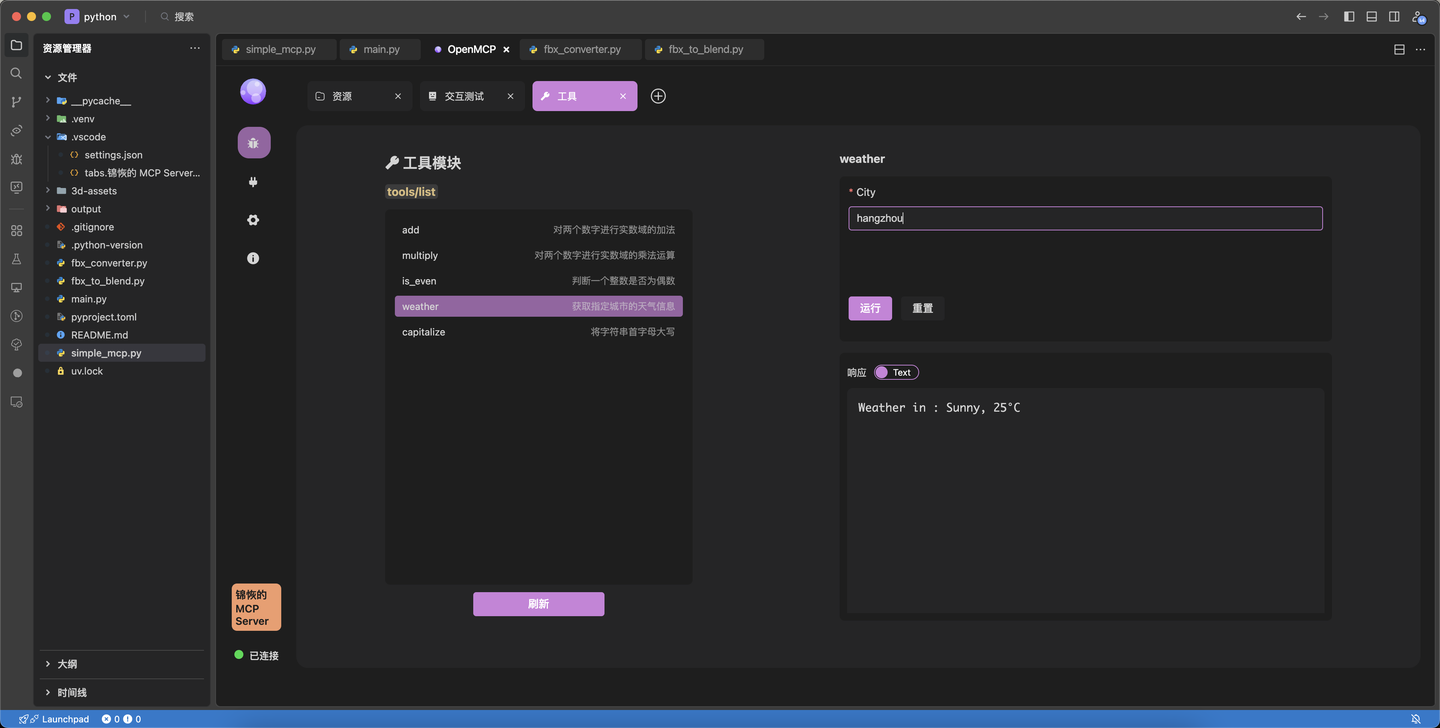
Interactive Testing
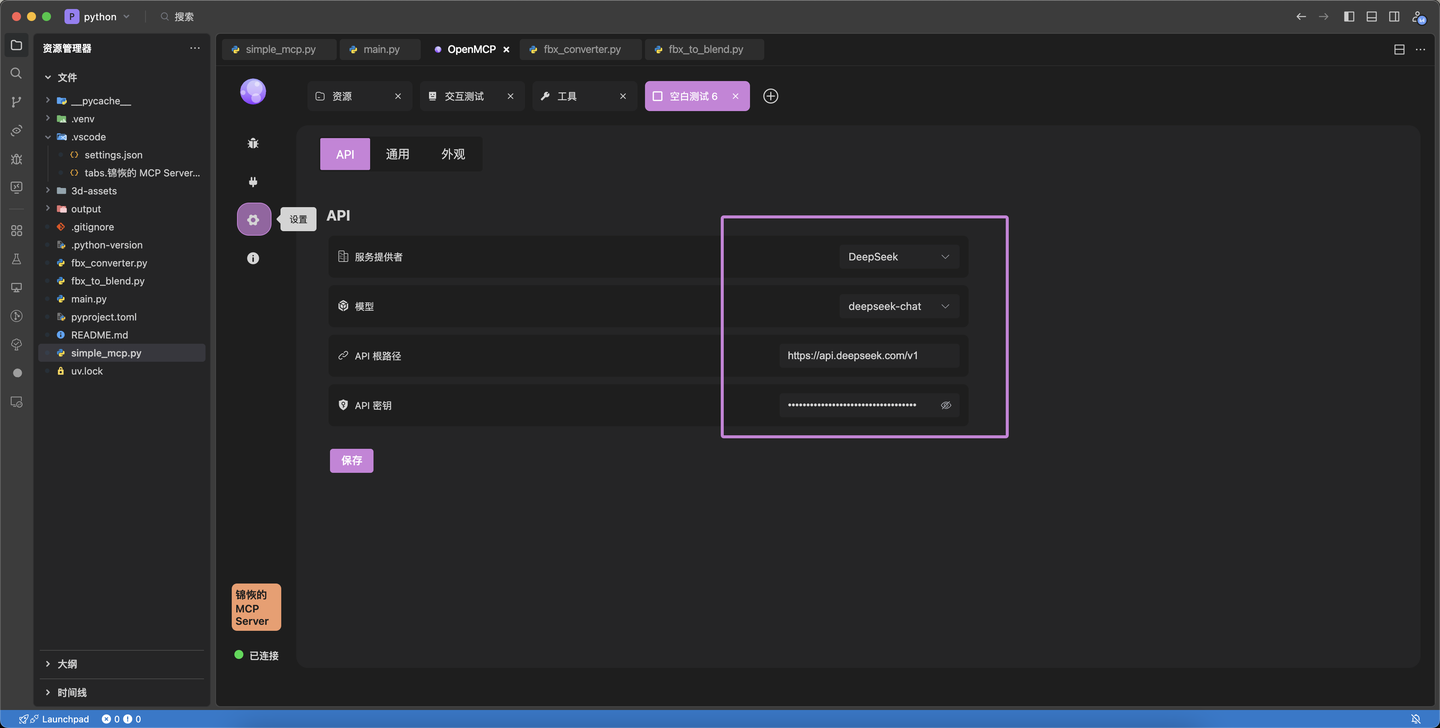
Configure your LLM API in OpenMCP:
Test without tools:
What's the temperature in Hangzhou?
Then with our weather tool enabled:
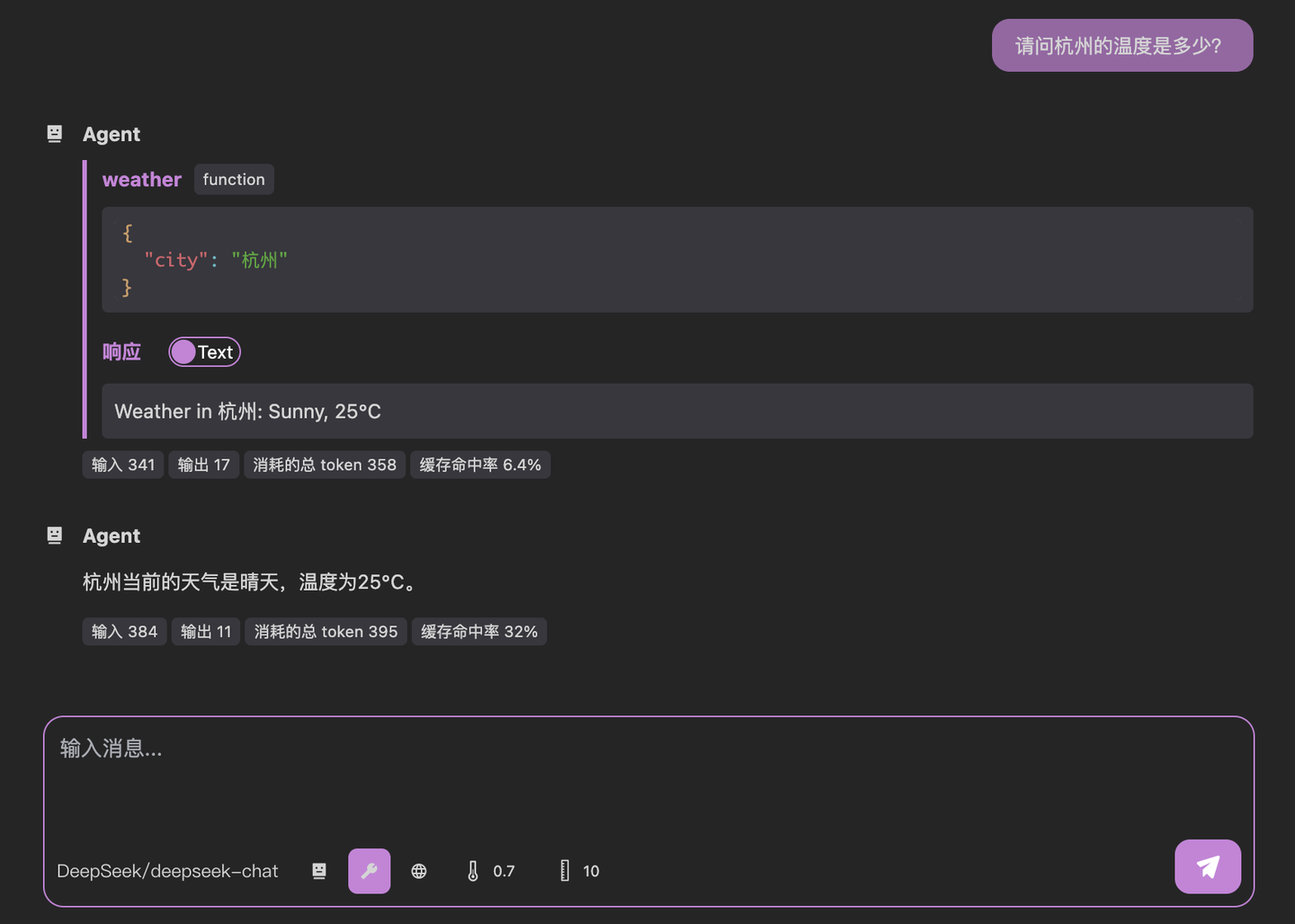
Notice the two-step process:
- LLM calls our weather tool with
{"city": "Hangzhou"} - Our server responds with formatted weather data
- LLM generates final answer
Production-Ready Implementation
Here's a complete weather implementation using a real API:
import requests
import json
from typing import NamedTuple, Optional
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
class CityWeather(NamedTuple):
city_name_en: str
city_name_cn: str
city_code: str
temp: str
wd: str
ws: str
sd: str
aqi: str
weather: str
def get_city_weather(city_code: str) -> Optional[CityWeather]:
"""Get weather by city code"""
try:
url = f"http://d1.weather.com.cn/sk_2d/{city_code}.html"
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0...",
"Host": "d1.weather.com.cn",
"Referer": "http://www.weather.com.cn/"
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
content = response.text.encode('latin1').decode('unicode_escape')
json_str = content[content.find("{"):]
weather_data = json.loads(json_str)
return CityWeather(
city_name_en=weather_data.get("nameen", ""),
city_name_cn=weather_data.get("cityname", "").encode('latin1').decode('utf-8'),
city_code=weather_data.get("city", ""),
temp=weather_data.get("temp", ""),
wd=weather_data.get("wd", "").encode('latin1').decode('utf-8'),
ws=weather_data.get("ws", "").encode('latin1').decode('utf-8'),
sd=weather_data.get("sd", ""),
aqi=weather_data.get("aqi", ""),
weather=weather_data.get("weather", "").encode('latin1').decode('utf-8')
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Weather query failed: {str(e)}")
return None
mcp = FastMCP('Weather MCP', version="1.0.0")
@mcp.tool(
name='get_weather_by_city_code',
description='Get weather by city code (integer)'
)
def get_weather_by_code(city_code: int) -> str:
weather_data = get_city_weather(str(city_code))
return str(weather_data)
Key Notes:
- Use
inttype for numeric IDs to ensure proper JSON serialization - Follow Python naming conventions for tool names
Final Test
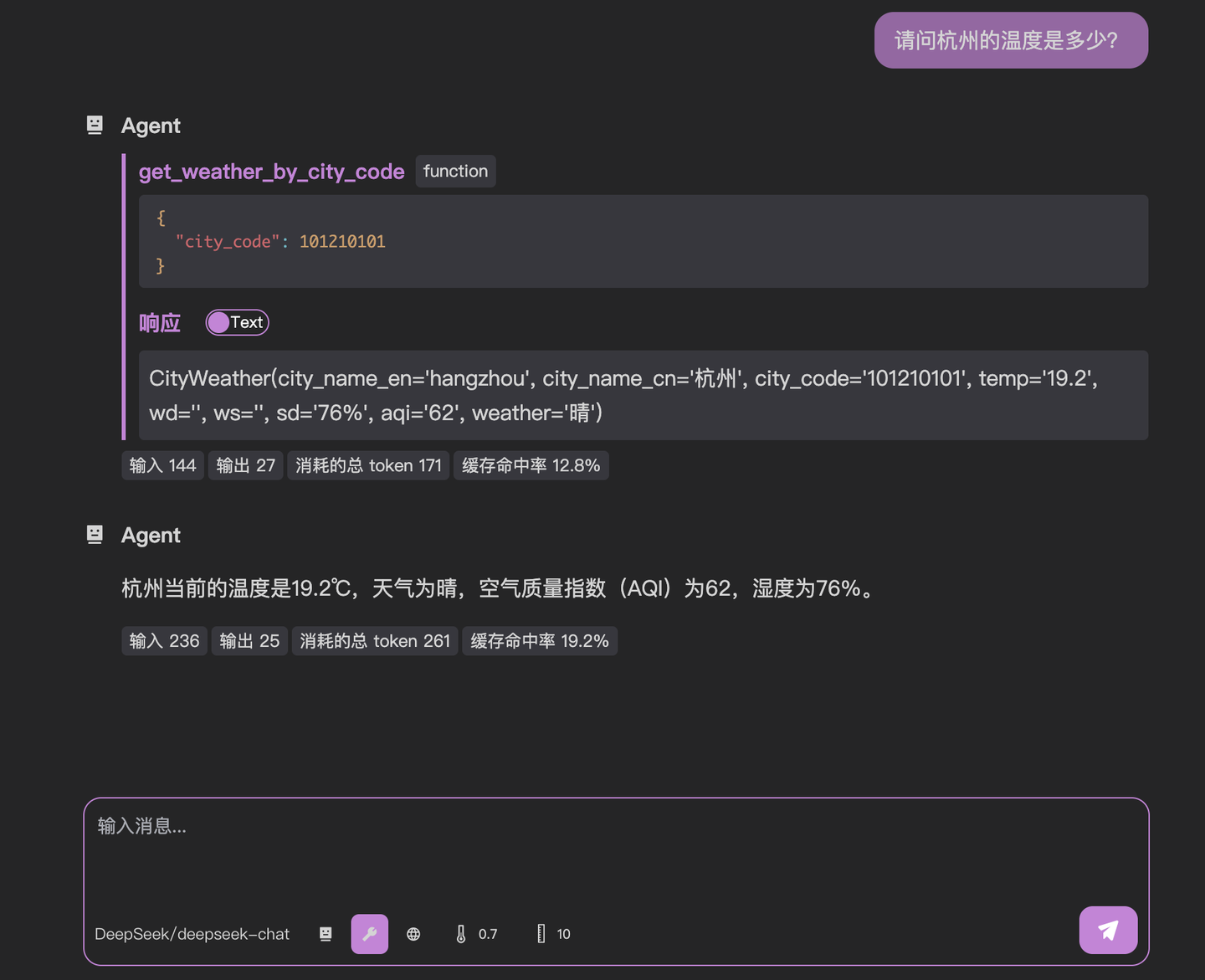
Success! We've built a fully functional weather MCP service. For production deployments, consider using SSE connections for better scalability (covered in future tutorials).
OpenMCP GitHub: https://github.com/LSTM-Kirigaya/openmcp-client